Politics
Report: $15 minimum wage bill would benefit 20.7 million workers
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Published
8 years agoon

Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis aut rerum necessitatibus saepe eveniet ut et voluptates repudiandae sint et molestiae non recusandae. Itaque earum rerum hic tenetur a sapiente delectus, ut aut reiciendis voluptatibus maiores alias consequatur aut perferendis doloribus asperiores repellat.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
“Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat”
Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit, sed quia consequuntur magni dolores eos qui ratione voluptatem sequi nesciunt.
Et harum quidem rerum facilis est et expedita distinctio. Nam libero tempore, cum soluta nobis est eligendi optio cumque nihil impedit quo minus id quod maxime placeat facere possimus, omnis voluptas assumenda est, omnis dolor repellendus.
Nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Neque porro quisquam est, qui dolorem ipsum quia dolor sit amet, consectetur, adipisci velit, sed quia non numquam eius modi tempora incidunt ut labore et dolore magnam aliquam quaerat voluptatem. Ut enim ad minima veniam, quis nostrum exercitationem ullam corporis suscipit laboriosam, nisi ut aliquid ex ea commodi consequatur.
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti quos dolores et quas molestias excepturi sint occaecati cupiditate non provident, similique sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollitia animi, id est laborum et dolorum fuga.
Quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur.
You may like
-


Mayors agree, Congress should invest in affordable housing
-


Congress rolls out ‘Better Deal,’ new economic agenda
-


Illinois’ financial crisis could bring the state to a halt
-


Ruth Bader Ginsburg optimistic ‘over the long haul’ for US
-


Poll: Virginia governor’s race in dead heat
-


House panel to consider bill to revamp DHS cyber team
Politics
Geopolitical Fallout: The Israel–Iran Conflict and Its Implications for India
Published
5 days agoon
June 18, 2025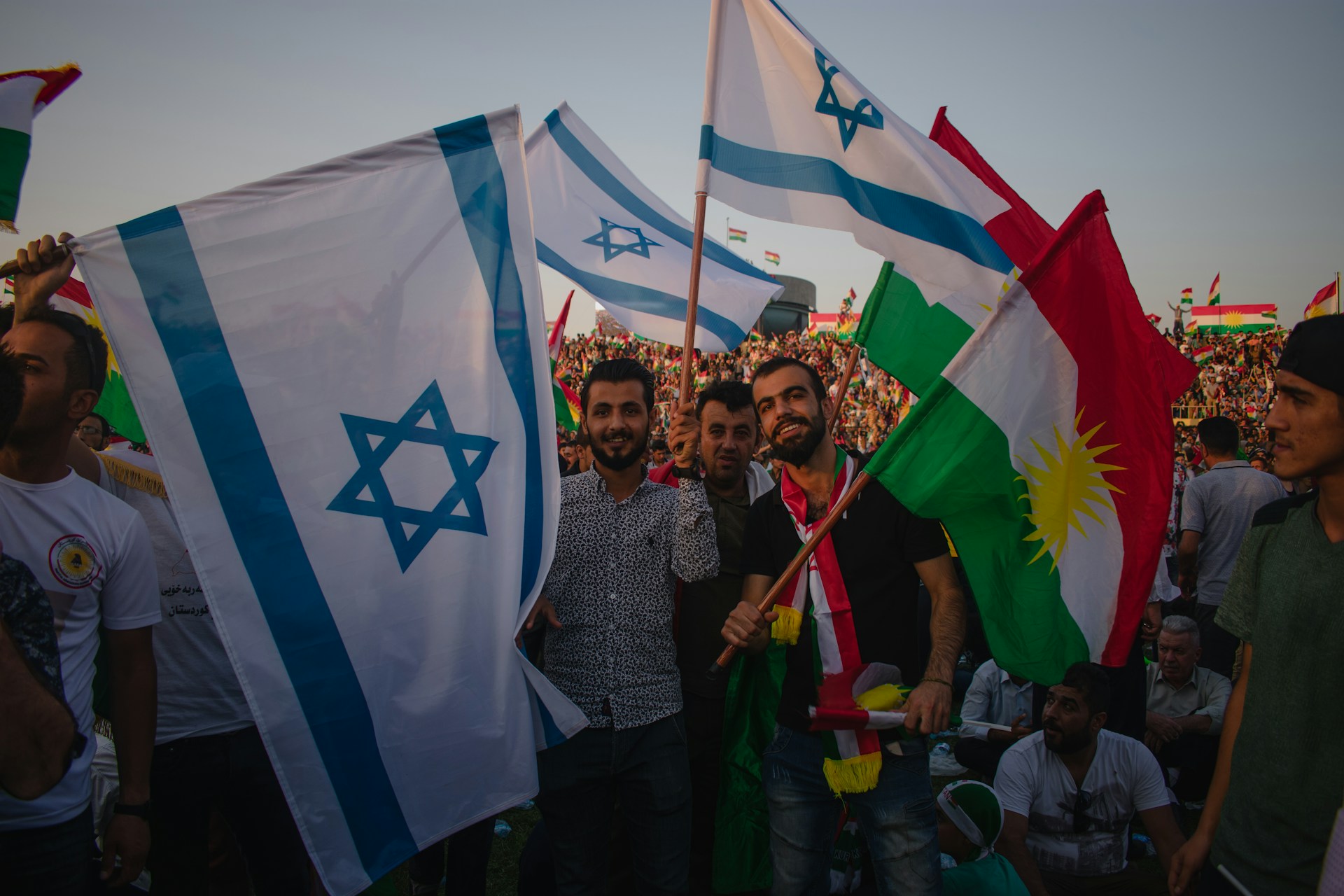
Geopolitical Fallout: The Israel–Iran Conflict and Its Implications for India
By the Editorial Board
The Sentinel Review | International Affairs Desk
As Israel’s “Operation Rising Lion” unfolds, the Middle East stands at a pivotal crossroads. With air supremacy over Iran already claimed and deep strikes conducted on its nuclear and military infrastructure, the conflict may appear to be tilting towards Israel. Yet the outcome remains uncertain—its implications for India profound.
Chapter 1: Israel’s Tactical Superiority, Iran’s Asymmetric Resilience
In the volatile theatre of the Middle East, few rivalries are as consequential and enduring as that between the State of Israel and the Islamic Republic of Iran. This is not merely a clash of two regional powers, but a protracted contest between conventional tactical superiority and asymmetric strategic resilience.
Over the past two decades, Israel has consistently demonstrated an unmatched military and technological edge, leveraging cutting-edge capabilities in intelligence, cyber operations, and airpower. The Israeli Air Force (IAF) operates the F-35I “Adir”, a customized variant of the American stealth fighter, allowing it to strike with precision while evading sophisticated radar systems—critical in missions across Syria and beyond. Israeli intelligence, credited with a deep penetration into Iranian nuclear planning, stunned the world in 2018 when Mossad agents exfiltrated 50,000 documents and 163 CDs from a Tehran warehouse—exposing the scope and scale of Iran’s nuclear ambitions.
Moreover, Israel’s operational history features strategic preemptive strikes, including the bombing of Syria’s Al-Kibar reactor in 2007 (Operation Orchard) and hundreds of targeted attacks on Iranian weapons convoys and depots in Syria in recent years. These operations, often carried out without Israeli casualties, demonstrate high levels of precision signal intelligence (SIGINT) and real-time surveillance.
In the digital domain, Israel’s collaboration with the United States in launching the Stuxnet worm—a cyber-weapon that sabotaged centrifuges at Iran’s Natanz facility—remains a landmark in state-sponsored cyber warfare. The sophistication of that attack set the precedent for digital espionage and industrial sabotage in the 21st century.
However, Israel’s superior firepower and stealth do not guarantee strategic dominance. Iran’s strength lies not in symmetry, but in survival and sustained disruption.
Iran has built a multi-layered deterrence matrix. Its nuclear infrastructure, buried deep within mountain ranges in Fordow and Natanz, is designed to withstand conventional bombing. According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Iran continues to develop advanced IR-6 centrifuges in protected facilities. These underground bunkers are reinforced and difficult to neutralize even with the GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator, raising questions about the limits of kinetic options.
Perhaps more significantly, Iran commands a transnational axis of influence. Through its “Axis of Resistance”, Tehran has entrenched itself across the region:
- Hezbollah in Lebanon maintains an arsenal of over 150,000 rockets, including precision-guided munitions aimed at Israel.
- The Houthis in Yemen have struck targets in Saudi Arabia and the UAE with Iranian-supplied drones and missiles.
- Shiite militias in Iraq and Syria, including Kataib Hezbollah and Liwa Fatemiyoun, have conducted operations against both U.S. and Israeli interests.
Iran’s response strategy is deliberately indirect and distributed—what analysts call “strategic patience.” It absorbs losses, retaliates through proxies, and thrives in the grey zones of hybrid warfare. It is not merely a matter of endurance, but of leveraging unrest—sectarian, political, or economic—to maintain ideological momentum across the Arab world.
Furthermore, Iran has invested heavily in cyber capabilities. Reports from the U.S. Cyber Command and Israeli cybersecurity firms point to an uptick in Iranian digital attacks targeting water infrastructure, hospitals, and private sector systems in Israel. In 2020, a cyberattack on Israeli water treatment plants, attributed to Iranian actors, prompted a retaliatory Israeli strike on Iran’s Shahid Rajaee port system, briefly halting operations.
The Nature of Victory
The metrics for success are markedly different for both sides.
Israel’s goal is not conquest, but containment—to delay or derail Iran’s nuclear breakout capability, dismantle weapons shipments, and prevent the consolidation of a second front in Syria or Lebanon. It seeks tactical victories with strategic implications.
Iran, conversely, defines victory as survival under siege. By enduring sanctions, assassinations (like that of nuclear scientist Mohsen Fakhrizadeh), and cyberattacks, Tehran projects resilience. It survives not just to outlast, but to outmaneuver—by turning every Israeli strike into a recruitment poster and every regional crisis into ideological capital.
This asymmetric duel is unlikely to culminate in a definitive battlefield showdown. Rather, it will unfold in the shadows of covert operations, through contested airstrikes, proxy escalations, and cyber intrusions. In this long war of nerves, both Israel and Iran have demonstrated that power is not just what you have, but how patiently and precisely you wield it.
Chapter 2: Regional Fallout: A Wider War or Contained Chaos?
The specter of a direct confrontation between Israel and Iran is no longer confined to speculative war games or classified think tank simulations. With a regional landscape already saturated by proxy militias, asymmetric warfare, and deep-seated ideological rifts, the consequences of even a limited escalation could ripple far beyond the immediate theatre of operations. The Middle East—already fragile from years of insurgencies, coups, and sectarian divisions—may be on the precipice of a wider conflict.
At the heart of the tension lies a complex paradox: both Israel and Iran have compelling reasons to avoid full-scale war, yet their tools of deterrence—proxies, preemptive strikes, and covert operations—often heighten the risks of unintended escalation. The question is not just whether a war is likely, but whether the region is structurally prepared to absorb the shock if it happens.
The Trigger Points: Proxy Fire, Regional Flames
A direct military exchange would not be isolated between Tel Aviv and Tehran. The geography of retaliation is transnational, shaped by Tehran’s extensive proxy network and Israel’s forward defense posture.
1. Hezbollah: The Second Front from the North
Lebanon’s Hezbollah remains the most potent Iranian proxy. With an estimated arsenal of over 150,000 rockets, including precision-guided munitions (PGMs) capable of reaching deep into Israeli territory, Hezbollah could rapidly escalate a northern front. The 2021 war games conducted by the IDF envisioned simultaneous missile strikes from Lebanon and Gaza, a scenario that significantly strains Israel’s Iron Dome and David’s Sling defense systems.
Hezbollah’s Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah has repeatedly warned that any Israeli strike on Iran will be treated as a regional attack, promising “a unified response”. With Hezbollah embedded within civilian infrastructure in Lebanon, a war would likely cause massive civilian displacement and casualties, risking another humanitarian crisis.
2. Yemen and Iraq: Peripheral Fronts, Central Risks
Iran could activate its influence in Yemen and Iraq, pressuring U.S. and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) interests. The Houthi movement in Yemen, aligned with Tehran, has already demonstrated the capacity to strike Saudi Aramco facilities, as seen in the 2019 Abqaiq-Khurais attacks, temporarily knocking out 5% of global oil supply.
In Iraq, Iranian-backed militias under the umbrella of al-Hashd al-Shaabi (Popular Mobilization Forces) have previously launched rockets at U.S. installations, including Erbil and al-Asad airbase. An escalation could see coordinated assaults on American military and diplomatic targets, drawing Washington deeper into the conflict.
Potential for a Pan-West Asian War
Should these dominoes fall in quick succession, a localized conflict could metastasize into a region-wide confrontation. The United States, despite its stated pivot to Asia, maintains over 40,000 troops across the Middle East, with major bases in Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait. Any attack on U.S. assets would necessitate a response, expanding the war theater.
Meanwhile, Saudi Arabia and the UAE, already targeted by Iranian drones and missiles, might join the fray—either in retaliation or defense. The Gulf’s proximity to Iran’s Strait of Hormuz, through which one-fifth of the world’s oil flows, turns any escalation into a global energy and economic crisis.
Even Turkey and Russia, each with strategic interests in Syria and Iraq, could be pulled into a diplomatic—if not kinetic—quagmire, depending on the conflict’s trajectory.
The Case for Containment: Strategic Restraint Amid Tactical Aggression
Yet despite the combustible conditions, both Israel and Iran may choose containment over escalation. Neither power seeks a war that would imperil their domestic stability.
Israel’s Calculus
Israel’s military doctrine relies on superior technology and quick, decisive operations. However, a multi-front war would severely test even its well-resourced defense systems. IDF leadership is acutely aware of the risks of being overstretched, particularly with Gaza, the West Bank, Syria, and Lebanon all potential sources of conflict. Moreover, with an economy heavily reliant on technology and global integration, a prolonged war would have major fiscal repercussions.
Iran’s Dilemma
For Iran, a large-scale war threatens not only its military assets but its very regime stability. With an economy battered by U.S. sanctions, a depreciating rial, and mounting public discontent—as seen during the 2022–23 protests following Mahsa Amini’s death—the regime is navigating a precarious balance between ideological rigidity and practical survival.
An Israeli bombardment of oil infrastructure or nuclear sites could provoke internal unrest, and the IRGC (Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps) knows that urban warfare on Iranian soil is a red line few in Tehran want to cross.
The Real Danger: Proxy-Triggered Escalation
History shows that wars often begin not with intention, but with miscalculation. In June 1914, a Serbian nationalist’s assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand triggered a cascade of alliances and mobilizations that led to World War I. The Middle East today is no less entangled—an ecosystem of proxies, militias, alliances, and informal pacts where one misfired rocket or retaliatory drone strike can spiral out of control.
As academic Vali Nasr noted in a recent panel at the Brookings Institution, “The Middle East doesn’t explode—it leaks into war. Conflict creeps forward until someone crosses a threshold they didn’t realize was there”.
The question is not just how to win the next battle—but how to design escalation ceilings that all sides tacitly recognize.
Between Fire and Restraint
The region stands at a critical juncture. While strategic logic favors containment, tactical provocations—from proxies or rogue actors—may force the hands of larger powers. The world must watch not just Jerusalem or Tehran, but also Sanaa, Baghdad, Beirut, and the Golan Heights. It is there, in the peripheries, that the next war may begin—not by declaration, but by detonation.
Certainly. Below is a professionally expanded editorial analysis suitable for the international economy or strategic affairs section of a leading newspaper. It incorporates verified data, credible sources, and nuanced geopolitical context to highlight India’s economic vulnerability amid West Asian instability.
Chapter 3: Economic Tremors: India’s Crude Reality
As tensions in West Asia inch closer to the brink of open conflict, India—Asia’s third-largest economy—finds itself exposed to a critical vulnerability: oil dependency. With over 80% of its crude oil requirements met through imports, the Indian economy is acutely sensitive to geopolitical disruptions, particularly those in the Gulf region, from where it sources nearly two-thirds of its energy needs.
At the heart of this risk is the Strait of Hormuz, a narrow but vital maritime chokepoint between Oman and Iran. Roughly 20% of the world’s seaborne oil—nearly 17 million barrels per day—passes through this corridor. It also serves as India’s main conduit for imports from Iraq, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Kuwait. Any disruption—whether due to conflict, sabotage, or even the threat of Iranian retaliation—could reverberate sharply through India’s economic landscape.
Shockwaves of a Strait Shutdown: Sector-by-Sector Breakdown
Even a temporary closure of the Strait or a credible threat thereof could send Brent crude prices surging past $100/barrel, triggering a cascade of economic consequences for India:
1. Oil Marketing Companies: Shrinking Margins
Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) like Indian Oil Corporation (IOCL), Bharat Petroleum (BPCL), and Hindustan Petroleum (HPCL)—which dominate India’s fuel distribution—often absorb price volatility due to state-mandated price controls on petrol, diesel, and LPG.
When global oil prices spike, their gross refining margins (GRMs) contract. In FY23, BPCL reported a sharp decline in GRM despite higher throughput, attributed largely to global price swings. In a high-price environment without matching retail adjustment, these firms operate at a loss—fueling balance sheet pressures.
2. Rupee Depreciation: Capital Outflows, Import Costs
A surge in oil prices intensifies India’s current account deficit (CAD). In 2022, a mere $10 rise in crude prices translated into an additional $15 billion CAD burden for India. As dollar demand spikes to pay for oil, the rupee weakens, exacerbating inflation and reducing investor confidence.
Recent episodes—such as the Russia–Ukraine conflict in 2022—saw the INR fall to a historic low of ₹83.29/USD amid rising crude benchmarks. A prolonged West Asia conflict could replicate or even worsen these conditions.
3. Inflation Surge: Fuel, Food, Freight
Fuel price hikes have a second-order inflationary effect across transportation, food supply chains, and industrial production. As diesel becomes more expensive, freight and agricultural logistics pass the cost to consumers. In India’s inflation basket, transport and food carry over 50% weight, meaning crude spikes have an outsized effect.
According to RBI projections, a $10/barrel increase in crude oil pushes headline inflation up by 30-40 basis points. Such increases pose dilemmas for monetary policy, especially when the RBI is walking a tightrope between inflation control and growth stimulation.
4. Fiscal Deficit: Subsidy Overhang and Welfare Pressure
India’s centrally managed fuel subsidy regime, though streamlined in recent years, may need temporary reactivation during oil shocks. Subsidies for LPG and kerosene, critical for lower-income households, could balloon unexpectedly.
In FY22, the government allocated ₹6,517 crore for petroleum subsidies. However, a crisis scenario could push this figure upwards significantly, inflating the fiscal deficit, which already stood at 5.8% of GDP in FY24, and may threaten the government’s budget consolidation path.
Strategic Limitations: No Easy Cushion
Unlike the U.S. or China, India lacks expansive energy buffers. Its Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR) capacity stands at only 5.33 million tonnes—about 9.5 days of import cover at current levels. Even combined with industry-held reserves, India’s total stockpiles offer less than a month’s security—woefully insufficient in case of a prolonged Gulf disruption.
This shortfall means India must look beyond stopgap measures and move toward structural energy diversification.
Policy Imperatives: From Risk Mitigation to Energy Transition
India’s vulnerabilities are not new, but today’s geopolitics make the need for diversification more urgent than ever. Key strategic levers include:
🔹 Diversifying Oil Suppliers
India has already increased crude imports from Russia, which became its top supplier in 2023 due to discounted Ural oil amid Western sanctions. Additionally, India has signed exploration pacts with Guyana, Brazil, and Nigeria, reducing its over-reliance on West Asia.
🔹 Energy Hedging Mechanisms
Oil PSUs must expand their use of financial hedging tools to lock in prices. While such mechanisms are already employed, they remain limited. Greater transparency and coordination among refiners could mitigate revenue volatility.
🔹 Accelerating Renewables
India is targeting 500 GW of non-fossil energy capacity by 2030, including solar, wind, and green hydrogen. However, the transition must also focus on grid integration, domestic manufacturing, and EV adoption to reduce long-term hydrocarbon dependency.
Preparing for the Next Shock
India’s growth story is intricately linked to energy security. As West Asia teeters on the edge of escalation, New Delhi must proactively shield its economy from oil shocks—not reactively absorb them. With smart diplomacy, diversified sourcing, strategic foresight, and clean energy innovation, India can mitigate its crude reality and chart a more resilient path forward.
Below is a refined and expanded editorial suitable for publication, embedding deeper analysis, current context, and reputable citations.
Chapter4: India’s Strategic Balancing Act: Navigating Between Israel and Iran
India’s foreign policy often reads like an intricate dance—a calibrated balance between sometimes competing powers. Nowhere is this more evident than in its simultaneous embrace of deepening ties with Israel and historic engagement with Iran. As Delhi strides across a shifting geopolitical landscape, a prolonged Israel–Iran confrontation risks upsetting this delicate equilibrium.
Partnership with Israel: Defense, Cyber, Technology
Over the past two decades, India has forged a robust defence and technological partnership with Israel:
- The acquisition of advanced Barak‑8 surface‑to‑air missiles, co‑developed by India’s DRDO and Israel Aerospace Industries, has significantly enhanced the Indian armed forces’ air defence capabilities.
- Collaboration spans missiles, radars, UAVs, and joint R&D in AI, robotics, quantum tech, including defense agreements formalized in 2021 .
- Cybersecurity cooperation is flourishing: bilateral exercises, threat‑intelligence sharing, and public‑private ventures harness Israel’s tech innovation and India’s IT skill base .
This partnership underpins India’s tightening security architecture—strategic, operational, and digital.
Engagement with Iran: Energy, Infrastructure, and Strategic Access
At the same time, Iran remains essential to India’s broader strategic vision:
1. Energy Security
Iran has been a vital source of discounted crude oil, critical amid global price volatility and sanction‑driven shifts.
2. Chabahar Port & Central Asian Access
The Chabahar Port project is the cornerstone of New Delhi’s strategy to diversify trade and transit routes:
- Operated under a 10‑year India‑Iran agreement, it forms part of the International North‑South Transport Corridor (INSTC), opening a direct lane to Afghanistan and Central Asia—bypassing Pakistan.
- India has invested over $370 million, including wheat shipments and humanitarian aid, with cargo throughput rising sharply in recent years.
- India’s NSA Ajit Doval’s May 2025 talks with his Iranian counterpart reaffirmed both sides’ commitment to infrastructure collaboration, including INSTC and regional stability.
3. Broader Connectivity & Diplomacy
Through Chabahar and related corridors, India supports Afghan access to global markets while countering regional Chinese influence—especially the Gwadar port .
Delicate Diplomacy: Walking the Tightrope
Historically, India has upheld a policy of strategic equidistance—drawing closer to Israel for defence and technology, while prioritizing ties with Iran for energy, connectivity, and regional reach.
India’s role in the I2U2 alliance (India–Israel–UAE–USA) emphasizes cooperation in semiconductors, agriculture, and water innovation, showcasing strong alignment with Western democracies. Simultaneously, Delhi remains engaged with Iran through platforms like BRICS+, and by safeguarding investments in infrastructure such as Chabahar and INSTC.
Potential Stress Point: Escalation in Israel–Iran Tensions
A prolonged Israel–Iran conflict could force India into a painful diplomatic recalibration:
- Pressure may rise to take sides—supporting Israel’s right to protect itself versus Iran’s calls for solidarity among Global South and energy-importing nations.
- Any overt tilt toward one could strain relations with the other, impacting military cooperation with Jerusalem or trade and access projects via Tehran.
Strategic Imperatives for India
To navigate this geopolitical crossfire, India should consider:
- Reaffirm neutral engagement with both powers, emphasizing peace, dialogue, and stability.
- Rebalance trade and energy portfolios, expanding oil ties beyond the Gulf.
- Insulate key projects like Chabahar through renewed diplomatic frameworks, legal strength, and multilateral support.
- Expand defense partnerships beyond Israel to include other global suppliers, reducing dependency.
- Deepen regional alliances, including South Asia, Central Asia, and the Gulf, to diffuse strategic pressure.
India’s balancing act—leveraging Israel’s technological prowess while relying on Iran for strategic connectivity—illustrates the complexity of 21st-century realpolitik. As the Israel–Iran rivalry intensifies, New Delhi’s ability to remain non-aligned yet engaged will be tested like never before. The strategic challenge is stark: preserve ties and projects without choosing sides, ensuring continued progress on both defense and development fronts.
Chapter 5: Cybersecurity and Maritime Infrastructure Risks
The strategic fallout from a widened Israel–Iran war is not limited to oil markets and kinetic fronts—it could spill into cyber and maritime domains, where infrastructure vulnerabilities prismatically amplify regional risks.
Maritime Cyber-Threats: From Ships to Subsea Backbones
Recent analyses indicate that Iranian and Iran-backed actors have demonstrated new capabilities to disrupt maritime operations, with implications for India’s trade lifelines.
- In early 2025, the hacking group Lab Dookhtegan claimed responsibility for disabling communications across 116 Iranian-flagged vessels, disrupting logistics and signaling a capacity for large-scale maritime cyber intrusions.
- The Nordic Maritime Cyber Resilience Centre notes that states like Iran are developing tools to hack ballast systems, jam navigation, and hijack ship systems—a tactic that could imperil vessels en route to or from Indian ports during regional escalation.
- Even civilian ships—both cargo and fishing fleets—are increasingly exploited for espionage or sabotage, compounding risk to India’s merchant marine and import/export lifelines .
Undersea Cable Vulnerabilities: The Hidden Shock
India’s digital resilience hinges on undersea cables that ferry 99% of intercontinental internet traffic, including vast volumes of financial, trade, and governmental data.
- In March 2024, Houthi missile strikes in the Red Sea—backed by Iran—led to the sinking of the MV Rubymar and severed four vital subsea cables, temporarily disrupting internet traffic from Africa to Asia and beyond.
- Faults exposed by such incidents spotlight the vulnerability of cable chokepoints in the Red Sea and the Arabian Sea, both critical to India’s connectivity and trading infrastructure .
- The risk landscape spans from accidental damage by ceremonial shadow fleets to purposefully engineered threats in the grey zone—ensuring disruptions could be strategically timed to coincide with wider conflict.
Cyber-Retaliation: Beyond Physical Infrastructure
Iran’s cyber arsenal, honed since the era of Stuxnet, now encompasses advanced persistent threats (APTs) capable of targeting critical infrastructure—energy grids, financial networks, even maritime systems.
- U.S. and allied cyber advisories consistently warn that IRGC-affiliated groups exploit operational technology, VPN weaknesses, and industrial control systems against Western, Gulf, and allied digital infrastructure.
- Studies forecast that, in response to Western cyber pressure, Iran is likely to conduct proportionate cyber strikes through proxies, focusing on financial, trade, transport, and digital targets outside traditional battlefields.
- Experiments in electromagnetic interference targeting vessel GPS/AIS systems off Iran’s coast suggest the ability to misdirect or disable shipping—capabilities which could affect Indian-bound maritime traffic.
India’s Strategic Cyber & Maritime Defence Posture
As Indian trade and digital flow pivot through Middle East chokepoints, Delhi must fortify defences on multiple fronts:
1. Maritime Cyber Resilience
- Roll out maritime cyber protocols for national-flagged and private vessels—mandatory cyber hygiene standards, incident monitoring, and coordinated drills.
2. Undersea Cable Protection
- Collaborate with telecom operators to implement cable risk mapping, proactive monitoring, and joint investment in rapid sub-sea repair infrastructure—leveraging global best practices .
3. Cybersecurity Preparedness
- India’s CERT-In, along with the NCIIPC and Defence Cyber Agency, should escalate monitoring of maritime, energy, and financial systems, backed by threat intelligence cooperation with allies like the US, Israel, and Gulf nations.
4. Strategic Diplomacy & Alliances
- Push for multilateral cable zone protections via embassies and international partners, securing the Suez–Mozambique–Mumbai–Singapore axis.
- Explore joint naval-cyber taskforces with maritime neighbours to defend flagship trade routes.
Invisible Fronts in a Visible Conflict
In a region cheered on by headlines of bombs and missiles, the quieter arenas of cyber and maritime infrastructure are just as vulnerable—and disruptive. Any escalation in Israel–Iran hostilities threatens not just barrels of oil but lines of code, fiber optics, and sea lanes that power India’s economy.
India must urgently bridge the gap between diplomacy and digital defenses. In a future of “smart” ships and automated systems, the next crisis may emerge not from a battlefield, but from a breached firewall—or a severed cable underneath the deep sea.
Politics
The Strategic Quagmire: Why Russia Is Prolonging the Ukraine War
Published
5 days agoon
June 18, 2025
Editorial | The Strategic Quagmire: Why Russia Is Prolonging the Ukraine War
By the Editorial Board
More than three years into the Russia-Ukraine war, the world continues to grapple with a haunting question: why hasn’t Russia, with its overwhelming military superiority, brought the conflict to a decisive end? Ukraine, though resilient and bolstered by Western aid, remains battered. Major cities lie in ruin, its economy has shrunk drastically, and millions have been displaced. From a purely military lens, the odds have long been in Moscow’s favour. Yet, the war drags on.
This apparent paradox is not born of Russian incapability, but of calculated intent.
A War of Attrition, Not Annihilation
Russia has not miscalculated its military capacity. Instead, it has chosen a war of attrition over a war of conquest. A prolonged campaign allows Moscow to drain Ukraine’s military resources, inflict sustained psychological pressure on its population, and gradually reduce Western public support for Ukraine’s cause. The Kremlin believes it can outlast both Kyiv’s resistance and the West’s attention span.
Controlling the Escalation Ladder
A full-throttle military offensive to “finish off” Ukraine would almost certainly raise the risk of direct NATO intervention or massive Western retaliation. By maintaining a calibrated level of intensity, Russia avoids triggering thresholds that could internationalise the conflict beyond its control. This war is being fought not just in trenches but on the escalation ladder—step by step, move by move, just below the point of no return.
Political Objectives Trump Military Gains
Putin’s war is not about land alone. It is about identity and influence. His goal is to dismantle the notion of Ukraine as a sovereign, Western-integrated democracy. A swift victory would not erase that idea. But a long, exhausting conflict could discredit it—painting Ukraine as unstable, unviable, and too costly a partner for the West. It is a psychological war as much as a territorial one.
Domestic Consolidation through Perpetual War
For the Kremlin, the war serves a powerful domestic function. It has created a rally-around-the-flag effect, suppressing internal dissent and boosting nationalistic fervour. A prolonged conflict offers a continuous narrative of victimhood, resistance, and greatness—central to Putin’s leadership mythology. Ending the war could force Moscow to face difficult post-war questions at home, including reconstruction, economic fatigue, and reintegration of battle-hardened veterans.
Strategic Disruption of the West
This conflict is also about geopolitics. By keeping Ukraine in limbo, Russia forces NATO to remain entangled, expends U.S. and European resources, and delays the pivot to Asia. It also tests the unity of European nations—many of whom face domestic backlash over rising defence spending and energy costs. The longer the war continues, the more frayed Western unity becomes, or so the Kremlin believes.
Weaponisation of Time
Russia is weaponising time as a force multiplier. The longer the war lasts, the greater the war-weariness among Western democracies governed by electoral cycles. Moscow is betting that political changes in the West—especially a shift in U.S. leadership or weakening of European resolve—could result in waning support for Kyiv. In contrast, Putin faces no such term limits. He is prepared to wait out his adversaries.
Creating a “Frozen Conflict” Trap
By drawing the war into a long stalemate, Russia may be attempting to turn Ukraine into a de facto “frozen conflict” zone—similar to Transnistria, South Ossetia, or Donbas before 2022. Such unresolved conflicts sap a country’s sovereignty and deter foreign investment and institutional progress. In this model, Ukraine remains locked in instability, unable to join NATO or the EU, forever under Russia’s strategic shadow.
The Energy and Grain Gamble
Russia has used the war to manipulate global energy and food supplies, leveraging its control over oil, gas, and grain exports. A prolonged war maintains global economic uncertainty and inflationary pressures, which Moscow uses as bargaining chips in negotiations with countries across Africa, Asia, and even parts of Europe. A short war would relinquish this coercive advantage.
The Perils of Prolongation
This strategy is not without risk. Russia faces severe economic sanctions, increasing diplomatic isolation, and a costly drain on military and human resources. Morale among conscripts is fragile. Domestic discontent, though suppressed, simmers beneath the surface. Yet the Kremlin appears confident it can manage these pressures better than the democratic governments backing Ukraine.
What Lies Ahead
Russia’s protracted campaign is not a sign of weakness but of hybrid strategic thinking—where time, ambiguity, and exhaustion replace traditional notions of victory. The international community must understand that in this war, Russia is not looking for a swift win, but for a slow, corrosive shift in the geopolitical balance.
For countries like India—treading a fine line between strategic autonomy and principled diplomacy—this underscores the need to engage both East and West thoughtfully, without being pulled into reactionary alignments.
The tragedy, thus, lies not in Russia’s inability to end the war—but in its deliberate choice not to.
Published by the Editorial Board of Think Sentinel, committed to informed, balanced analysis in a rapidly polarizing world.
Politics
Mayors agree, Congress should invest in affordable housing
Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis aut rerum necessitatibus saepe eveniet ut et voluptates repudiandae.
Published
8 years agoon
July 25, 2017
Quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur.
Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis aut rerum necessitatibus saepe eveniet ut et voluptates repudiandae sint et molestiae non recusandae. Itaque earum rerum hic tenetur a sapiente delectus, ut aut reiciendis voluptatibus maiores alias consequatur aut perferendis doloribus asperiores repellat.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
“Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat”
Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit, sed quia consequuntur magni dolores eos qui ratione voluptatem sequi nesciunt.
Et harum quidem rerum facilis est et expedita distinctio. Nam libero tempore, cum soluta nobis est eligendi optio cumque nihil impedit quo minus id quod maxime placeat facere possimus, omnis voluptas assumenda est, omnis dolor repellendus.
Nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Neque porro quisquam est, qui dolorem ipsum quia dolor sit amet, consectetur, adipisci velit, sed quia non numquam eius modi tempora incidunt ut labore et dolore magnam aliquam quaerat voluptatem. Ut enim ad minima veniam, quis nostrum exercitationem ullam corporis suscipit laboriosam, nisi ut aliquid ex ea commodi consequatur.
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti quos dolores et quas molestias excepturi sint occaecati cupiditate non provident, similique sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollitia animi, id est laborum et dolorum fuga.


Geopolitical Fallout: The Israel–Iran Conflict and Its Implications for India

The Strategic Quagmire: Why Russia Is Prolonging the Ukraine War

Mobile Google CEO Promises 11 Daydream-compatible phones
Trending
-

 Fashion8 years ago
Fashion8 years agoThese ’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoThe final 6 ‘Game of Thrones’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 Fashion8 years ago
Fashion8 years agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Sports8 years ago
Sports8 years agoPhillies’ Aaron Altherr makes mind-boggling barehanded play
-

 Business8 years ago
Business8 years agoUber and Lyft are finally available in all of New York State
-

 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years agoDisney’s live-action Aladdin finally finds its stars
-

 Sports8 years ago
Sports8 years agoSteph Curry finally got the contract he deserves from the Warriors