WSU’s AI-Powered 3D Printing of Human Organs: A Preview of the Future
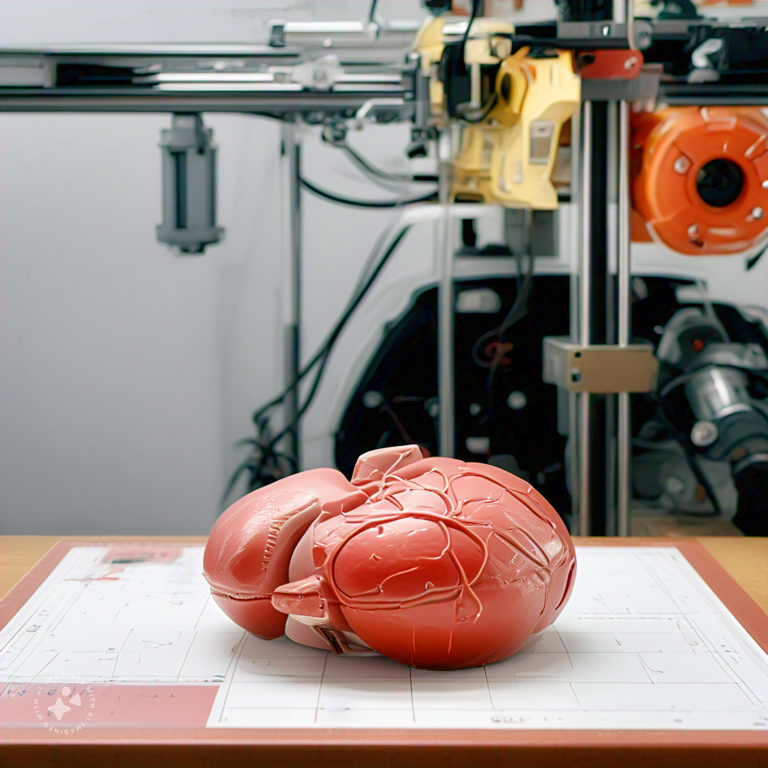
In a groundbreaking stride toward the future of medical science, researchers at Washington State University (WSU) are pioneering the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to 3D print human organs. This cutting-edge research, recently published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies, reveals a transformative approach that could reshape the landscape of healthcare, offering a promising solution to the global organ shortage crisis.
AI Revolutionizing 3D Printing
Artificial intelligence has already shown its potential in various fields, from enhancing workplace productivity to revolutionizing early cancer detection. Now, WSU researchers are taking this technology to new heights by applying it to the complex process of 3D printing human organs. The team has employed a sophisticated AI method known as Bayesian Optimization, which significantly enhances the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of creating intricate, lifelike human organ models.
This AI-driven approach marks a monumental leap in the field of biomedical engineering. The WSU team’s innovation not only improves the precision of 3D printing but also optimizes the entire process, reducing both time and costs. The potential to one day create fully functional human organs in a lab setting is no longer a distant dream but a plausible future scenario.
The Study’s Breakthrough Findings
The study conducted by WSU stands as a testament to the power of AI in overcoming the challenges associated with 3D printing complex structures. The researchers trained their AI algorithm to print the most accurate versions of kidney and prostate organ models. Astonishingly, the algorithm successfully produced 60 progressively refined versions of these organs, demonstrating the potential for AI to revolutionize the production of artificial organs.
This advanced technology could soon enable the creation of organ models that are not only visually accurate but also mimic the mechanical and physical properties of real human organs. Such advancements hold immense potential for medical applications, including surgical training and the evaluation of implant devices.
Beyond Medicine: Expanding Horizons
While the primary focus of this research is on medical applications, the implications of AI-driven 3D printing extend far beyond healthcare. Industries such as computer science, aviation, and automotive engineering could also benefit from the ability to produce highly complex and precise components using this technology. The adaptability of the AI algorithm, as demonstrated by its success in printing both prostate and kidney models with minimal adjustments, suggests a wide range of potential applications.
The WSU team’s innovation is not just about creating lifelike organ models. It’s about paving the way for a future where 3D printing can be used to produce functional human organs, potentially saving countless lives. The continued development of this technology could lead to a new era in which organ donation shortages become a thing of the past.
A Future Shaped by AI
As AI continues to evolve, its integration into the field of 3D printing promises to bring about unprecedented changes. Washington State University’s groundbreaking research offers a hopeful glimpse into a future where the combination of AI and 3D printing could revolutionize not just medicine, but multiple industries. The possibilities are vast, and the impact could be profound, making this one of the most exciting developments in recent years.

Average Rating